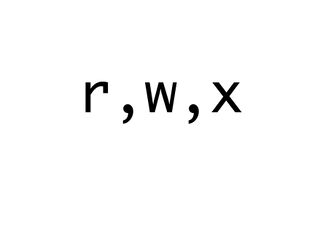A mouse, keyboard and collaborative text-editing demonstrated in Douglas Englebart’s “Mother of All Demos”, 1968
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 1: read, write, execute
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 2: legible vs readable
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 3: People read best what they read most
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 4: An annotated book
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 5: From the Books
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 6: DDC 000-099; Generalities
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 7: State Library of Victoria, Redmond Barry Reading Room
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 8: Traces of use
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 9: The Library is Open
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 10: Marginal Conversations workshop
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 11: Annotation pack
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 12: Performing annotations
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 13: Script from Marginal Conversations
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 14: Talking Clock (2015)
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 15: The Remington Standard Type-Writer
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 16: QWERTY layout
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 17: T Y P E W R I T E R
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 18: Douglas Englebart's "Mother of all demos"
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 19: Englebart's keyboard with mouse
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 20: Etherpad instance
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 21: Etherpad experiments
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 22: editorial, technical, social dimensions of text
-
-
-
-
-
Slide 1: read, write, execute
- -
-
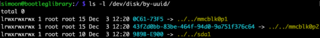
In computing, read, write, and execute are permissions that can be given to files by an administrator to user accounts, which specify how data can be used:
-
-
- read permissions allow you to read a file
-- write permissions allow you to change it, but not to run it
-- execute permissions allow you to run a file
-
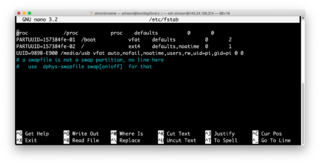
You are most likely familiar with the "read-only" permission.
-For example, a document with read-only permissions given to a user means that user can only read the document, and can't edit it.
-
I have chosen this title because for this presentation I want to focus on how the contingencies offered by interfaces for reading and writing produce a certain kind of reading or writing, and also a certain kind of reader or writer.
-
My main interest in this presentation is to describe through several examples, the political dynamics and particular affordances of different interfaces and sites for publication, and the subsequent techno-sociologial effects these have through the way they visualise reading, writing and making things public.
-
Interfaces for reading and writing are almost always visually-oriented, and their technical conditions determine how textual information is organised and processed.
-This promotes and encourages certain ways of writing and reading.
-
I will present examples from my own practice as an artist and graphic designer, and also some historical examples from computer science and engineering.
-
Beginning with the field of type design and typography, I want to talk about ideas of legibility and readability, which often precede notions of how written language should be visualised in graphic form.
-
-
-
Slide 2: legible vs readable
- -
-
Put simply:
-
legible = clear enough to read
-readable = being easy or enjoyable to read
-
Often someone will use illegibility as an excuse to argue against the use of a particular font or typeface. Physical limitations are certainly a factor in deciding how type should be shaped, down to the micro-level that scrutiny of readability brings, where enjoyment is hampered by exhausted eyes. A file can also be made readable by changing permissions. Allowing a file to be read has many other implications apart from the obvious visibility of content.
-
-
-
Slide 3: People read best what they read most
- -
-
There's a famous dictum in typographic history that states "People read best what they read most"
-This means that what is deemed "readable" is only so because of the prevalence of a particular font. And so, preference for certain fonts may derive from how commonplace they are within the reading environments we encounter them.
-
This statement was a call to arms for multiplicity of form in type design, to challenge this tendency for form to become flattened and homogenous in the name of "readability", but it also maintains that the way information is presented becomes monolithic, having its own, enclosed logic that is exclusionary to other systems or ways of doing.
-
The eye adjusts to expect certain things it has seen before, and this idea of "easy to read" is trainable, to a certain extent. We might think that a certain font is "neutral", this is because it has become invisible to us, and it is invisible to us because it is everywhere. It therefore doesn't stand out in a way that other typefaces do.
-So the main point I will try to make in this presentation is that the particular interfaces we commonly use for reading and writing train us to read and write in certain ways, ways which we will become efficient within.
-
When we shift to a different writing or reading interface, there is an adjustment, a period of discomfort as we adapt.
-We approach new interfaces through the lens of the one that preceded it, always likening it to what we are familiar with.
-The new interface presents new limitations, and also offer new, unexpected possibilities for how we imagine ourselves as participatory subjects, engaging with the text.
-
The discourse around reading and writing interfaces is vast, and I do not expect to be able to cover it comprehensively in this presentation.
-I can only hope to present a small overview on these interfaces, and how they visualise language, and in turn, how they create a new subjectivity in the reader or writer.
-
-
-
Slide 4: An annotated book
- -
-
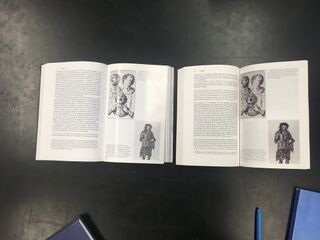
First, let's look at the book as a reading interface. What we call a "book" is most often a stack of pages that are fixed at one edge to form a spine.
-Reading a book is a haptic experience; the sense of touch is in many ways just as important as the sense of vision.
-Alongside this strong tactile interaction is also the inclination for a reader to engage with the text by writing directly onto the page.
-The interface of a printed book invites writing, in fact the very first books were written by hand.
-It is not uncommon to come across another reader's notes, annotations scribbled in the margins of a book.
-Annotation is primarily a strategy of reading comprehension, and there are many activities that fall under the umbrella of "annotation", including highlighting, underlining, glossing (which is writing explicatory texts that define unfamiliar phrases or words), as well as how pages are manipulated to mark text, for example, making a bookmark by folding the corner of a page in what is often called in English a "dog-ear".
-
Despite these annotations are made at different times, by different people unbeknownst to each other, their methods are often consistent with each other. Their annotations also often serve the same purpose, as a reformatting of the text that is read. So the function is sometimes editorial; highlighting or underlining is a way of drawing attention to part of the text that is relevant to the person who is reading it, giving them a way to return to it when scanning through at a later time.
-
Annotation also has a social function; inscribe the presence of reader within a book. The book then becomes a vehicle for a social paratext, one that lives alongside the source text, one that can be commented on by others. Sometimes these paratexts separate from the source and become texts of their own. Glossaries come from the practices established by medieval glossators, who wrote explanations of Roman law between the lines of manuscripts. The first dictionaries served a similar purpose.
-
Books held in public collections have travelled different paths through the hands of different readers. They acquire provenance and their own particular history through how they are used. A book printed, bound and distributed in an edition of many books, a multiple with the ambition to present its text as singular, becomes diversified through its use
-
-
-
Slide 5: From the Books
-
-http://simonbrowne.biz/projects/from-the-books-slv-rbrr-000-099/
-
From the Books is a research project conducted together with graphic designer Masaki Miwa. Together, we collected scans of any traces of use we found in a section of books from a public library in Melbourne, Australia. We then categorised them and made a catalogue which we self-published.
-
-
-
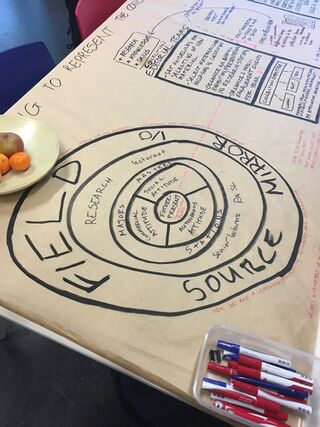
Slide 6: DDC 000-099; Generalities
- -
-
These books come from a section of a specific reading room in a specific library; the 000-099 section of the Redmond Barry Reading Room, at the State Library of Victoria. In Dewey Decimal Classification, 000-099 is titled "generalities", including books about bibliographic practices as well computer and information science, and also manuscripts and rare books; kind of a meta section on the library and how it organises information.
-
-
-
Slide 7: State Library of Victoria, Redmond Barry Reading Room
- -
-
The SLV is a very social place; visitors use the free wifi for study, and international students often use it to call their families overseas. Others do language lessons there and gather in social groups to share skills.
-It's not a sacred or quiet like a church, more like a train station in terms of its noise and activity. The SLV forecourt is a customary meeting place, people eat lunch there on the grass, on Sundays it is a speaker's corner, protestors gather there for demonstrations.
-
It illustrates well that public libraries do more than just make knowledge accessible, they also produce sociality. This sociality is reflected by the tendency for businesses to open in the periphery and capitalise on this foot traffic, or those that adopt library-like structures and practices (for example, cafes that offer free wifi or cosy nooks to read)
-
Here in Rotterdam this is also present - Starbucks has opened a store at the Bibliotheek Rotterdam, there is a cafe above Rotterdam Centraal Station that houses part of the same collection. There's even a cafe called "The Library" at Mathenesserplein
-
-
-
Slide 8: Traces of use
- -
-
Here are some examples of traces of use we found in the section of books we explored. We categorised them semantically under the following headings:
-
-
- ACCIDENTAL DOG-EAR
-- ANNOTATION
-- ASTERISK
-- BOOK PRICE
-- BOOKMARK
-- CIRCLED TEXT
-- CREASED PAGE
-- CROSS
-- DEAD ANT
-- DOG-EAR
-- ERASER RUBBING
-- ERRATA
-- FINGERPRINT
-- FOLD
-- HANDWRITTEN LETTER
-- INK BLOT
-- LIBRARY DOCUMENT
-- LIFTED PRINT
-- LINE
-- LOOSE PAGE
-- NOTEPAPER BOOKMARK
-- NOTES
-- PAGES REMOVED
-- POST-IT NOTE
-- RECEIPT BOOKMARK
-- REPLACED IMAGE
-- SCUFF
-- SMUDGE
-- SQUIGGLE
-- STAIN
-- STRIKETHROUGH
-- TICK
-- TORN PAGE
-- TORN PAPER BOOKMARK
-- UNDERLINING
-- WARPED PAGE
-- WEAR AND TEAR
-
The traces were largely mundane, but revealed a consensus of mark-making and annotation. We also found readers intentionally using the book as a vehicle to pass messages to other readers, such as a handwritten note someone had deliberately placed in a book.
-
This interest in annotation as a visualisation of reader's interaction with texts was developed further with a thematic project called "The Library is Open", conducted by Experimental Publishing in 2019. The Library Is Open was an afternoon of workshops in which we made visible the operations of libraries, including municipal, academic, and importantly, so-called "Shadow" libraries, which are ones that operate outside of legality, illegally distributing pirated copies of books.
-
-
-
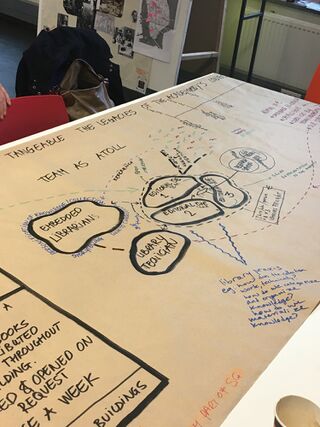
Slide 9: The Library is Open
- -
-
As part of "The Library is Open", I conducted a workshop called "Marginal Conversations" with two classmates, Artemis Gryllaki and Paloma Garcia.
-We held our workshop at a volunteer-run space in the inner west of Rotterdam, called "Leeszaal Rotterdam West".
-
Leezaal is a kind of 'reading room', a library that does not catalogue its books, nor record when they are borrowed. Anyone may pick up a book and walk out the door.
-The initiative began in 2013 when small local libraries in Rotterdam began to close, and the initators asked their local community two questions; 1) Do we need a library?, and 2) How can you contribute?
-
Leeszaal offers a safe space for members of the local community to gather, to learn languages and share skills, to read newspapers, learn how to use computers, use the internet, watch YouTube or just hang out. It's not a traditional library in any sense, but is sympathetic to many of the social democratic values of open access to knowlegde that public libraries embody.
-
-
-
Slide 10: Marginal Conversations workshop
- -
-
Marginal Conversations focused on reading and annotating together, and performing our annotations. We read and annotated an open letter called "In Solidarity with Library Genesis and Sci-Hub".
-
http://custodians.online/
-
This letter asks for pirate library practices to come out of the shadows, a bold move and demand for legitimacy and visibility
-
-
-
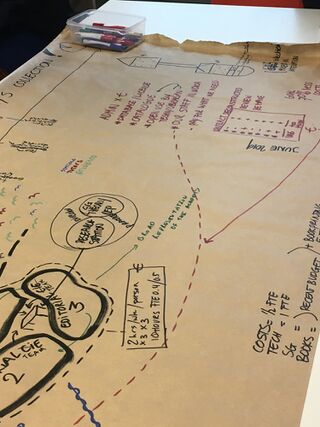
Slide 11: Annotation pack
- -
-
We made an annotation kit that contained the letter, a layer of carbon paper, and a sheet of translucent tracing paper. After reading and annotating the letter, we could compare our annotations by overlaying the tracing paper to create "heat maps" that established common areas of interest.
-
-
-
Slide 12: Performing annotations
- -
-
Then we rehearsed and performed our annotations, taking turns to read the letter while others reacted with their annotations.
-
-
-
Slide 13: Script from Marginal Conversations
- -
-
We made a recording of this performance, and then transcribed it into a script.
-
The flipping back and forth between oral and literate productions of texts is a strategy to discover the slippages in the memory of texts that occur when transcribing. Early media theory was particularly concerned with the gap between orality and literacy, and the effect writing has on the problem of memory. Writing as a technology had a considerable effect on how we think about memory and how we form cultural narratives. The view of memory as a container within which information can be stored is very much a post-literate idea, from this also comes the the notion of "verbatim" or "word perfect". This is because what is said can be recorded in written words and stored in a text, which can be checked against for discrepancies. Pre-literate cultures think of memory instead as commemorative, a communal act of remembering together through oral storytelling traditions.
-
Without a writing system in which memory can be stored and retrieved, events and narratives are seen as cyclical, and the notion of things "in their place" is ascribed to external forces like the seasons, the weather and time.
-
-
-
Slide 14: Talking Clock (2015)
- -
-
http://simonbrowne.biz/projects/talking-clock/
-
This is a work I made in 2015, called Talking Clock. I was interested in using the mechanism of a clock to produce language, including "real" and also "potential" words.
-I made a spreadsheet to work out the best combinations of letters to use on the flip cards, plotting combinations of letters, and mapped words I knew existed, words which were possible (following linguistic conventions), and words which were unlikely. In total I produced 72 cards, 12 for the left side of the clock (one for each hour in a 12-hour cycle), and 60 for the right side (one for each minute).
-
The clock displays, or "prints" 1440 words every day (1 per minute). It's very noisy, making a loud click every time a card flips over. It's very difficult to tell the time as the sequence of numbers are replaced by a different system of letters, but it's possible at least to know that the hour has changed, with a little time spent with the clock.
-There is a sense that the machine is writing the words, but they have been pre-selected by a human, myself.
-
When we encounter a new word in English, it's not always possible to know how to say it, especially in English, which has different standards, and borrows words from many other languages, so spelling and pronunciation are very different sometimes. This leads to the fluidity of "potential words". Because they isn't yet a consensus on their use, there also is no consensus on their pronunciation.
-
-
-
Slide 15: The Remington Standard Type-Writer
- -
-
The earliest transcription machines were ones that humans operated, becoming the transcriber.
-This lead to the invention of machines like typewriters, and practices like stenography, which were used in court cases to record proceedings.
-The need to type quickly, to keep up pace with speech and to record spoken language "verbatim" lead to the design of interfaces and systems that trained operators to use them efficiently
-
In the late 19th century came the emergence of typewriters, such as this one that was produced by the American company Remington.
-
-
-
Slide 16: QWERTY layout
- -
-
The layout of keys (now known as the QWERTY layout) was invented by Christopher Latham Sholes, who wanted to keep the typebars from clashing when the operator typed quickly.
-
He sold his design to the Remington Company, a typewriter manufacturer, who popularised it, selling their machine alongside typing courses that trained writers to use the layout, purporting it to be the best for rapid typing.
-
The QWERTY arrangement of the original Remington typewriter has remained virtually universal since the 1890s, even though more efficient arrangements have been developed. There is no particular reason why this convention has taken such a strong hold. Technological advances in machinery and electronics have rendered the problem Sholes was trying to solve redundant, but still it persists. If you've ever had to use a non-QWERTY keyboard, you may struggle.
-
-
-
Slide 17: T Y P E W R I T E R
- -
-
Reportedly the Remington Company also liked its product name, "type-writer," to appear acrostically in the top row.
-
Fast-forward to December 9, 1968, and computer engineer Douglas Englebart gave what is now known as "the mother of all demos" at a San Francisco computer conference.
-
-
-
Slide 18: Douglas Englebart's "Mother of all demos"
- -
-
He presented a demonstration that includes many features of computer engineering and publishing that we now take for granted, including the mouse, video conferencing, the modern desktop-style user interface, word processing and collaborative text-editing.
-
-
-
Slide 19: Englebart's keyboard with mouse
- -
-
About 26 mins into the presentation Englebart says "I don't know why we call it a mouse...it started that way and we never did change it."
-
While the mouse is a useful tool in modern desktop-style graphic user interfaces, text editors and computer terminal windows utilise the keys and forgo the use of a mouse.
-Text editors are used for a variety of writing applications, for example programming, and writing text documents, without the need to style it graphically.
-Most computer operating systems come with a text-editing program as part of the basic package of software (e.g. Mac has "TextEdit" and Windows has "notepad"). These programs are usually used by a single user at one time.
-
Some environments, such as the one Englebart demonstrates, are collaborative, allowing many users to write together in realtime.
-
-
-
Slide 20: Etherpad instance
-
- -
-
I'd like to talk about a collaborative writing environment that exemplifies the editorial, technical and social dimensions of text; the open-source software Etherpad. This software is a manifestation of what Englebart demonstrated in 1968, and through its interface and technical configuration offers an interesting twist on the notion of public space and the public it creates.
-
You can install etherpad-lite on a server, and host the software for yourself or others to use
-although most pads aren't indexed by search englines, they are 100% public, and editable to anyone who knows their URL.
-
It's a very dynamic writing environment, and environment in the sense of the combinations of technical conditions of hardware and software, and how users operate within it every key you press is recorded (including deletions), building a mind-boggling database in the background which you can track in the version history, import/export text.
-
The software automatically assigns authorship colours, users can change them and give themselves user names or remain "unnamed". Authorship in etherpad is blurry from the level of the user, but crystal clear from the level of the system administrator (can easily run searches on IP addresses).
-Interesting social protocols emerge from collaborative use of pads concerning conviviality (not so much spell-checking or correction). Misspelling is transgressive and signals the speller's marginal status, either preeducated, uneducated, or sloppy. Ignoring misspelling in favour of transcription, recording what is said quickly introduces a type of collective, consensual authorship.
-
New users react with either enthusiasm or suspicion - to the enthusiasts, it's exciting to collaborate in realtime, to others it's just a bit too public, everything you type can be seen as you type it.
-
-
-
Slide 21: Etherpad experiments
- -
-
Here is a series of solo experiments I conducted with Etherpad, where I wrote and edited text within constrained periods of time. Etherpad offers the potential for very quick visualisations of the writing and editing process through its autmoatically assigned authorship colours.
-
I was interested in seeing what happened when I visualised the writing and editing process. I wrote as multiple users, opening up a new tab in a private window each time and tricking the software into thinking I was a new writer, so it gave me new authorship colours.
-
This was a timed task, beginning with writing periods of 3 minutes, and a rest of 2 minutes. After 4 iterations, this shifts to 5 minutes for both respectively. I found I needed a bit more time as the text began to grow.
-
This experiment showed me that editing is a form of writing, like growing a tree and making furniture from it at the same time.
-
-
-
Slide 22: editorial, technical, social dimensions of text
- -
-
At the beginning of this presentation I described my interest in text and its overlapping dimensions; editorial, technical and social.
-
I will go into a bit more detail now to explain further:
-
-
- editorial: text is a sequence. A line of characters and spaces, the particular order that the writer sets these in. Text becomes an object, a carrier of thoughts and feelings, something that can be sent back and forth between participants in a conversation.
-- technical: text is a process. Messages and files that we share are text-based. A computer runs on software, programmed in encoded text, often the same characters that flicker before your eyes. Texts can be assembled on-the-fly as a machine reads scripts and writes output in response to input.
-- social: text is a framework. The English word "text" has roots in the Proto-Indo-European word teks-, meaning “to weave, to fabricate, to make; make wicker or wattle framework”. A piece of writing is a text, and so is a conversation; texts represent the exchange of shared concepts (words, signs, representations) woven into a fabric of communication. There is also an exchange between written and spoken texts; oral discussions which prompt writing, and writing which sparks conversations. Texts elicit further texts.
-
Etherpad exemplifies all three of these dimensions. The interface allows readers to become writers, and text editors, themselves. It uses the technicality of text-based software to record what is written, or deleted there in a process that is recorded in the version history. And when used collaboratively (which is what it is designed for, it creates a framework of shared concepts that come together into the one textual fabric.
-
What is important about this, as well as other open-source tools for reading and writing is that they offer the potential for us to develop our own particular ways of reading and writing. There is a lot more effort that is needed in order to not just read and write, but to also determine our own definitions of what is most readable, writeable and executeable.
+
diff --git a/tasks/Skimming.html b/tasks/Skimming.html
index ab1d98f..44a09c9 100644
--- a/tasks/Skimming.html
+++ b/tasks/Skimming.html
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@
-